Is The National Weather Service More Accurate Than Accuweather

The U.Southward. National Weather Service (NWS) is a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Many people rely on the National Weather Service'south forecasts in order to better anticipate what the weather will be like so they can plan out their days. But it'southward non uncommon to feel let downwardly by a forecast, peculiarly if y'all stop up getting caught in a rainstorm or snow flurry when you thought it was safe to get out your jacket at home. In this article, we'll explore the basics you should know about the NWS, compare the NWS to other big-name atmospheric condition sites and examine how accurate (and trustworthy) their forecasts really are.
Backside the Scenes of the National Weather Service: Satellites and Funding
The NWS'due south mission is to "to provide observations, forecasts, and warnings of weather, water and climate for the protection of life and property and enhancement of the national economy." The service is funded by the U.S. government. In 2021, the Biden assistants proposed the largest budget increase for NOAA to date, which brings the organization'south funding up to $6.nine billion. This funding will be partially used to ensure the NWS is able to continue its use of advanced engineering science to predict the conditions, which includes using ecology satellites.
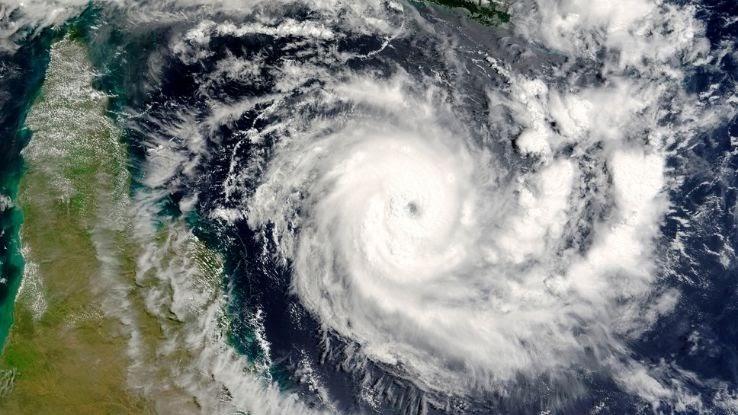

Satellites are instruments that provide data about the atmospheric conditions of the planet, and these are essential for accurately forecasting the atmospheric condition. NOAA uses three types of satellites to observe the conditions on Earth.
Geostationary Satellites
Geostationary satellites orbit World at the same speed every bit the planet, which allows them to collect virtually-continuous images of the same area. Considering they focus on one surface area, they also provide up-to-the-infinitesimal information on severe conditions. Forecasters utilize these data to determine how quickly a storm and other conditions conditions might grow and move.
Polar-Orbiting Satellites
A system of satellites called the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) orbits approximately 500 miles above Earth. Its satellites zoom around our globe 14 times each twenty-four hour period. Because they orbit between poles, the JPSS tin observe any area multiple times daily.
Satellites in polar orbit take the adequacy to monitor Earth'due south entire atmosphere at a high resolution. This can help forecasters determine tropical weather condition patterns, which tin can allow them to effectively predict long-term weather up to a week in advance.
Deep Space Satellite
The Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) orbits Earth virtually 1 million miles away from the planet, providing space conditions predictions and measuring how much solar energy the planet absorbs every twenty-four hour period. DSCOVR too measures ozone and aerosols, 2 factors that are essential for overseeing air quality.
How Authentic Are 10-Day+ Forecasts?
The NWS provides a number of unlike extended forecasts to help people better anticipate outdoor conditions for longer periods of time. These include yearly, 30–ninety-twenty-four hour period, two-calendar week and 10-solar day forecasts that aim to outline expected precipitation and temperature levels. According to NOAA's SciJinks learning website, 1-week forecasts are approximately 80% accurate, and v-twenty-four hours forecasts are approximately xc% accurate. However, a 10-day or longer forecast is simply accurate most half the time.

A weather condition model's unreliability can be attributed to both its mismatch to actuality and to atmospheric chaos. Conditions models rely on observations obtained from satellites, balloons and other outposts to provide initial impressions about conditions, and these methods are far from perfect.
However, forecasting is also dependent on analyzing past weather conditions and events and determining what patterns arise, then using information from those patterns to make highly educated guesses almost what will happen. Co-ordinate to SciJinks, "Since we can't collect information from the hereafter, models have to use estimates and assumptions to predict future weather. The atmosphere is changing all the fourth dimension, so those estimates are less reliable the farther yous become into the time to come." This accounts for the diminishing accuracy levels for extended forecasts.
The National Atmospheric condition Service vs. Other Top Weather Forecasters: The Battle for Accuracy
If y'all take several unlike weather apps on your smartphone, y'all've probably noticed that they all tend to evidence slightly unlike forecasts. Weather Hole-and-corner, Foreca Weather, OpenWeatherMap, The Weather Channel, AccuWeather and more are all competitors in forecast accuracy. Merely private forecasters — along with producing their own data — often rely on data provided by the NWS. So, which ones can you really trust?
To determine how the NWS compares to the balance, let's look at the top contender: AccuWeather. The main difference betwixt the two is that the NWS is funded past the regime, while AccuWeather is a role of the $7 billion private weather forecasting industry.
A 4-year analysis by independent forecast tracker Forecast Sentry looked at 120 million forecasts from over 1,000 locations globally. The results pinpointed AccuWeather as the nigh accurate provider of temperature, precipitation and wind speed forecasts for a one- to five-day forecast period.
Still, in 2015, the NWS decided it was time for a change. The organization ended upwards signing a licensing understanding with AccuWeather, which gave it the right to use two unique applied science patents. Although private agencies exercise use the NWS for some of their data, they're largely becoming more independent by developing their own (sometimes superior) technologies. This puts the NWS in an awkward position, as there's now an increasing need to continue to collaborate with private agencies in gild to ensure its service remains as accurate as possible.
NOAA has noted that American weather forecasts all fall behind in terms of accuracy when compared with European models. This is due to the fact that Europe allocates v times as many resources to weather research, while America tends to focus on parallel modeling programs.
So, Just How Accurate Are National Weather Service Forecasts?
It should be noted that, just like other weather services in the United States, the NWS can most accurately predict the conditions up to a week in advance. All the same, equally regime funding and collaboration with private forecast services continue to grow, the NWS continues to improve its accuracy and reliability.

It's no undercover that NOAA is well aware of the NWS's limitations in weather forecasting and is on a mission to create new technology that'll help amend weather forecasting with its $15 million Earth Prediction Innovation Center project. These efforts, combined with more extensive government funding initiatives, tin help ensure the NWS won't fall behind when compared to individual weather forecasters.
Is The National Weather Service More Accurate Than Accuweather,
Source: https://www.reference.com/science/national-weather-service-accurate?utm_content=params%3Ao%3D740005%26ad%3DdirN%26qo%3DserpIndex
Posted by: bradleybutch1981.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is The National Weather Service More Accurate Than Accuweather"
Post a Comment